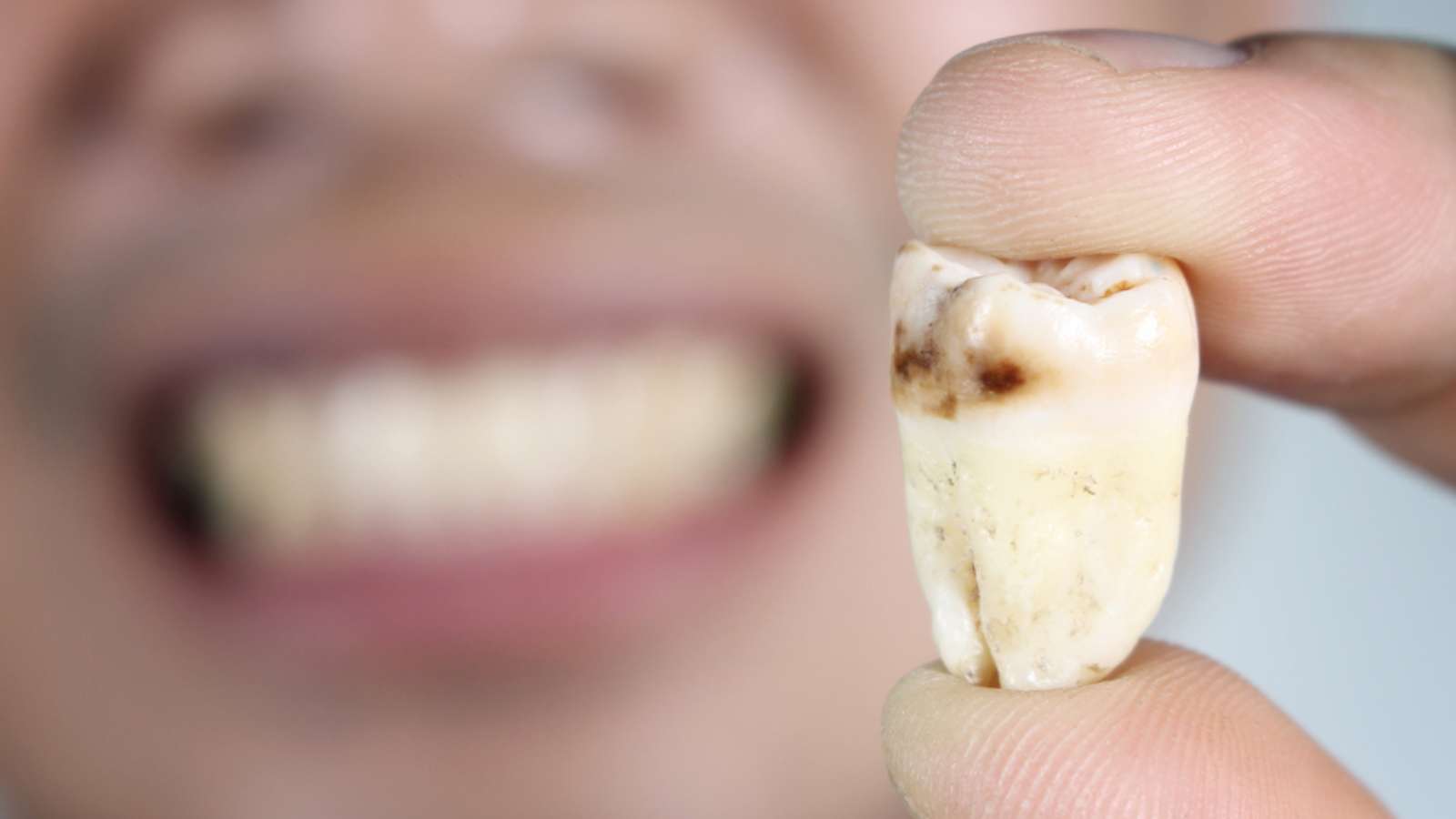
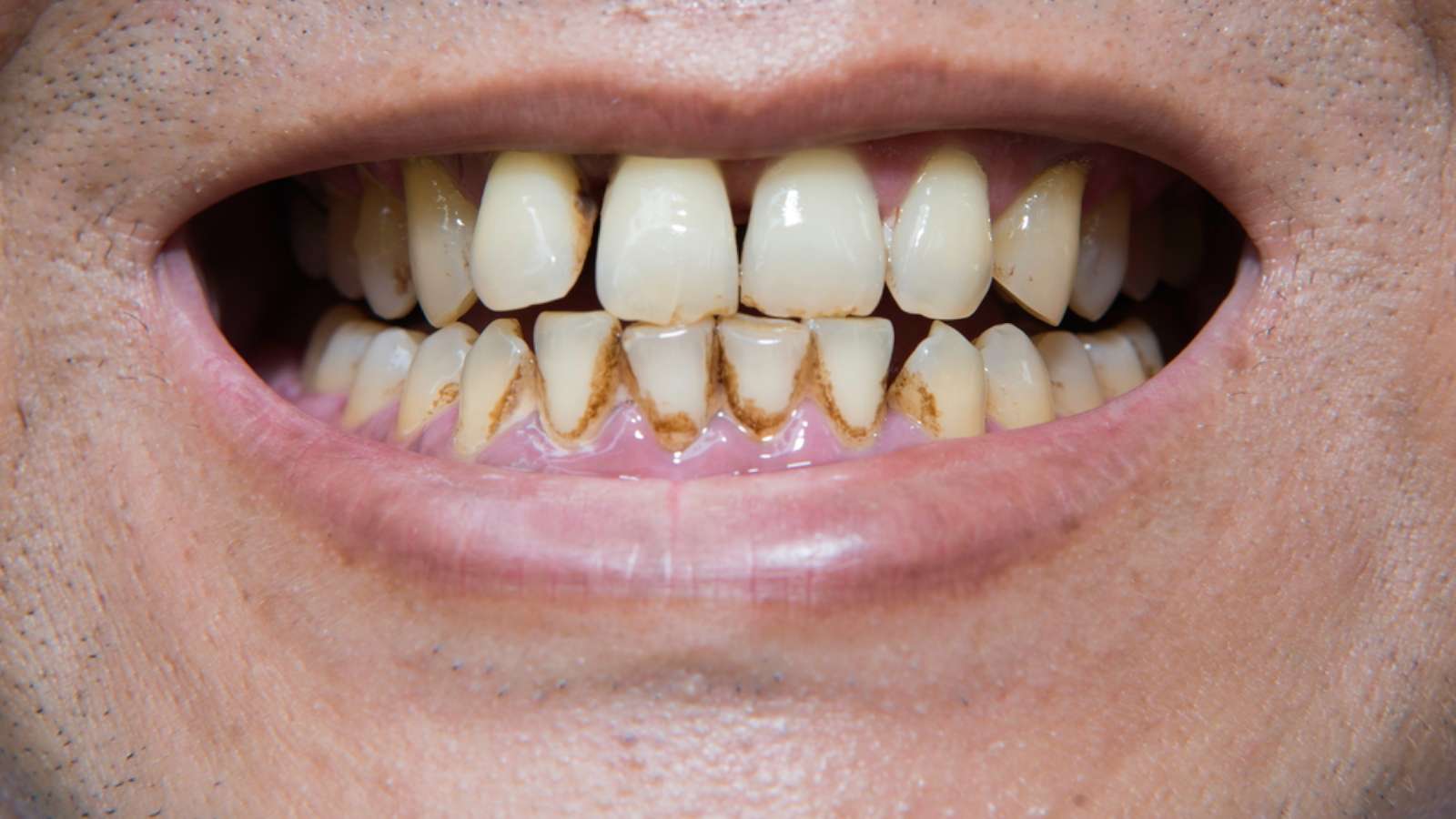
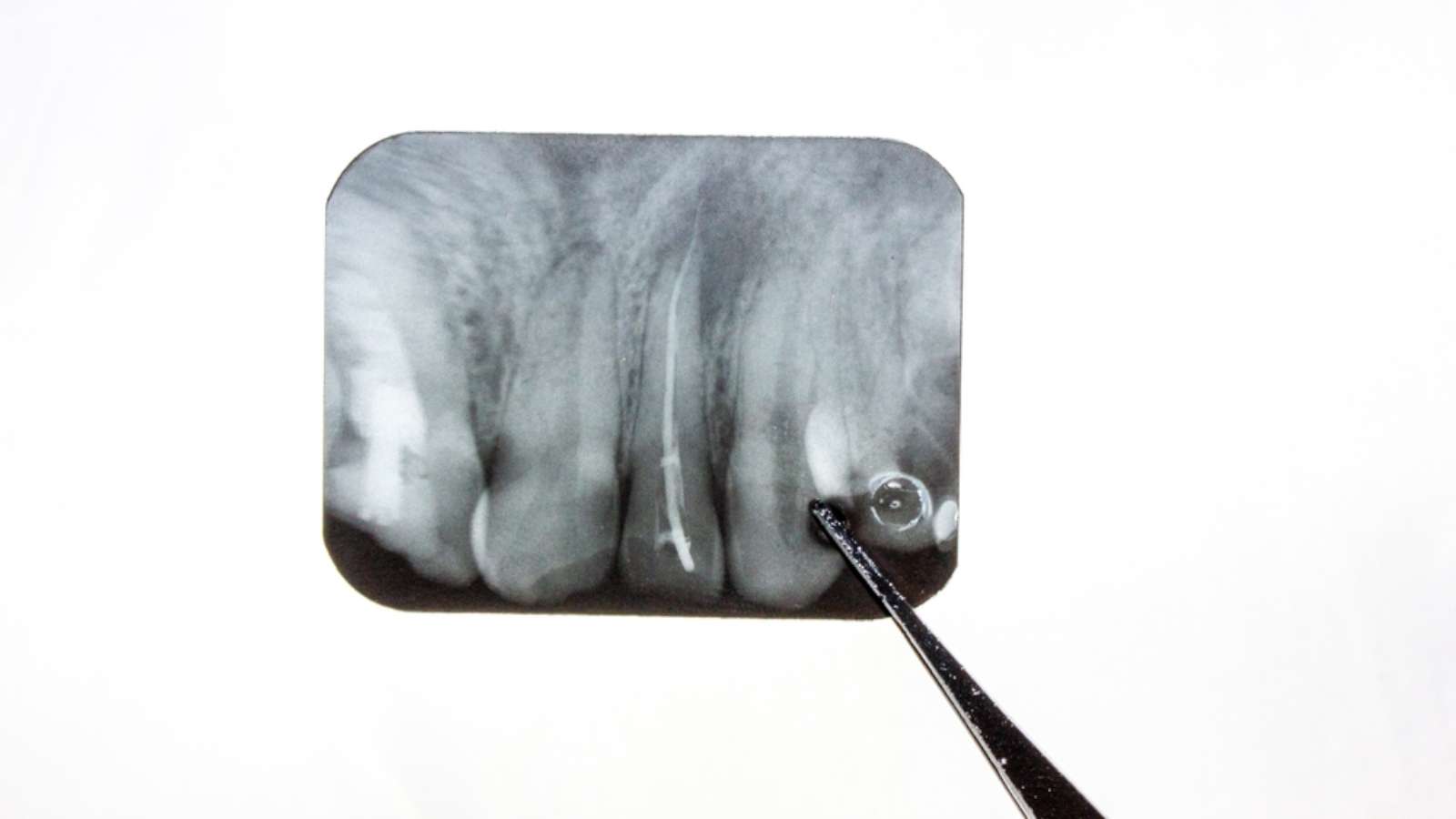
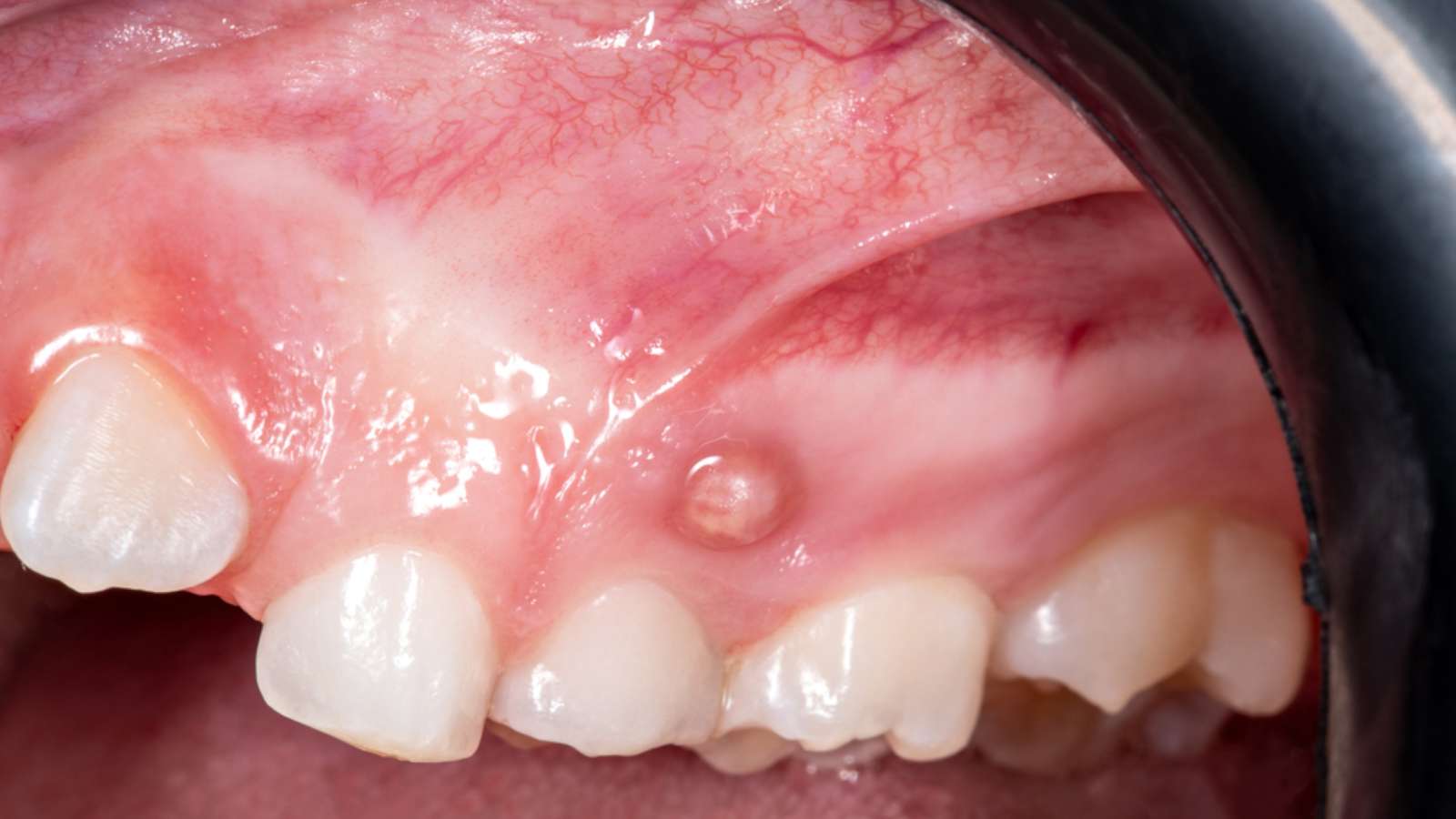
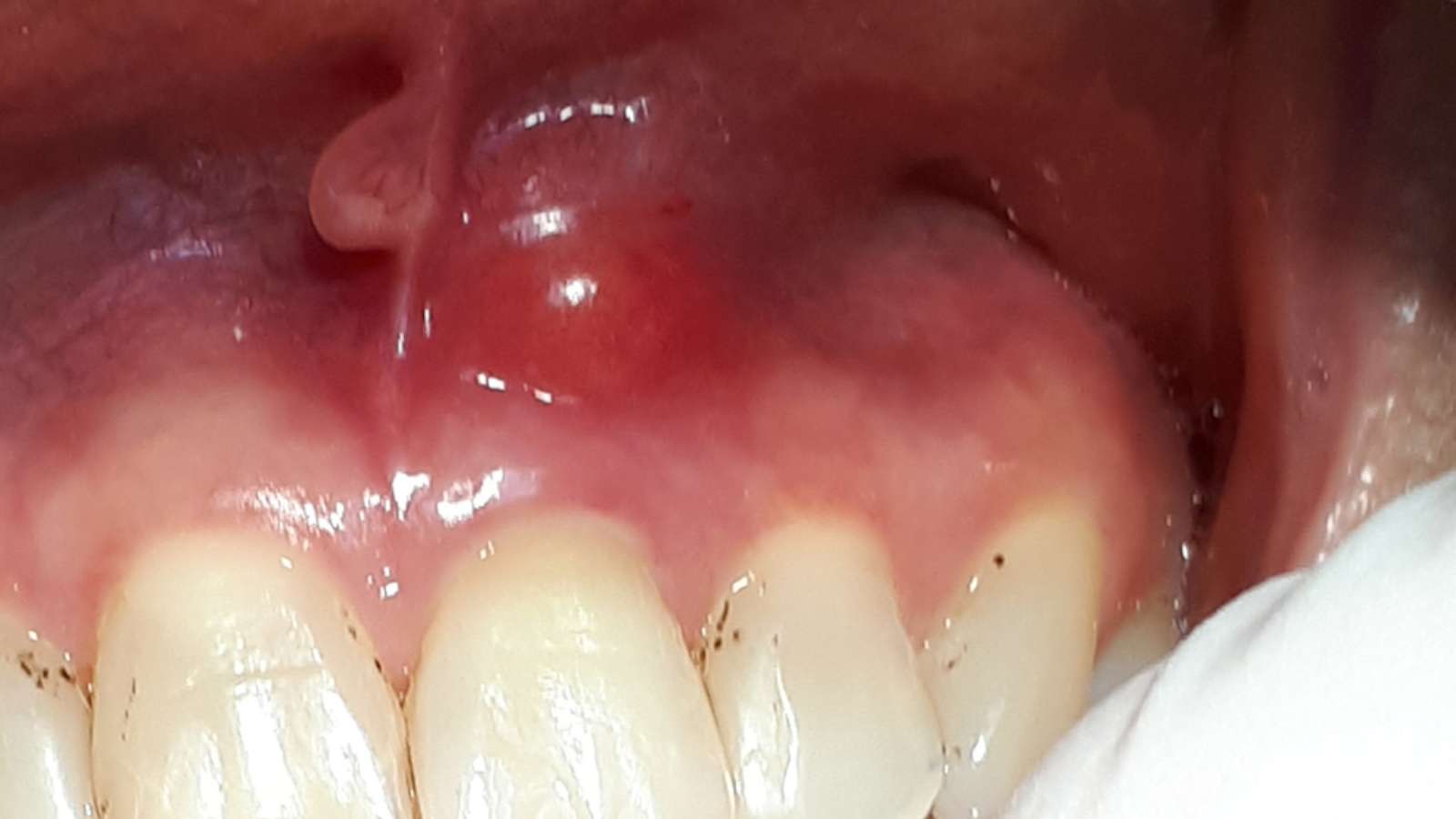
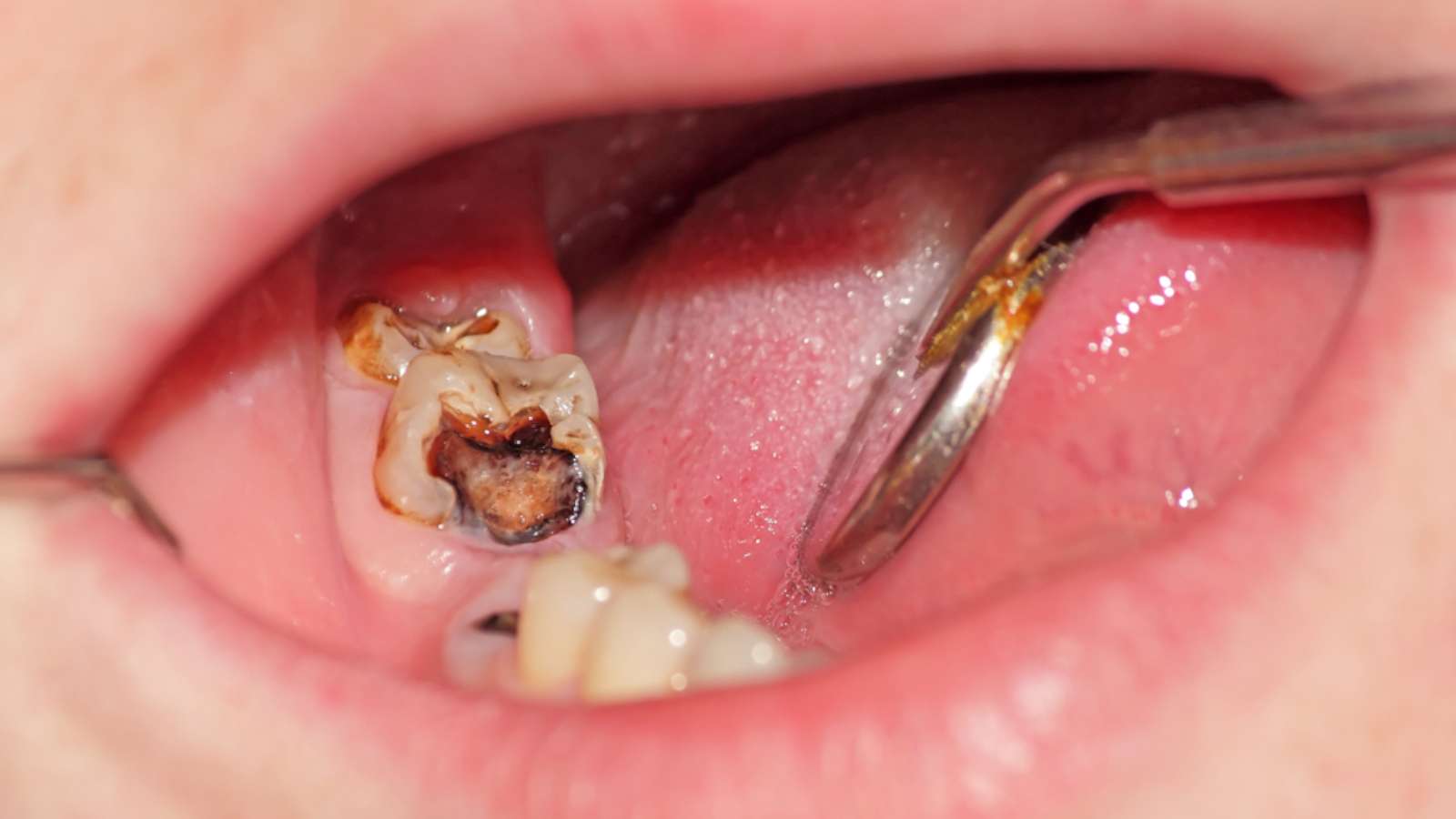
Involvement of cavities on the biting surfaces of teeth, such as:
1. Pits, fissures, buccal and lingual surfaces of premolars and molars.
2. Lingual surfaces of front teeth.
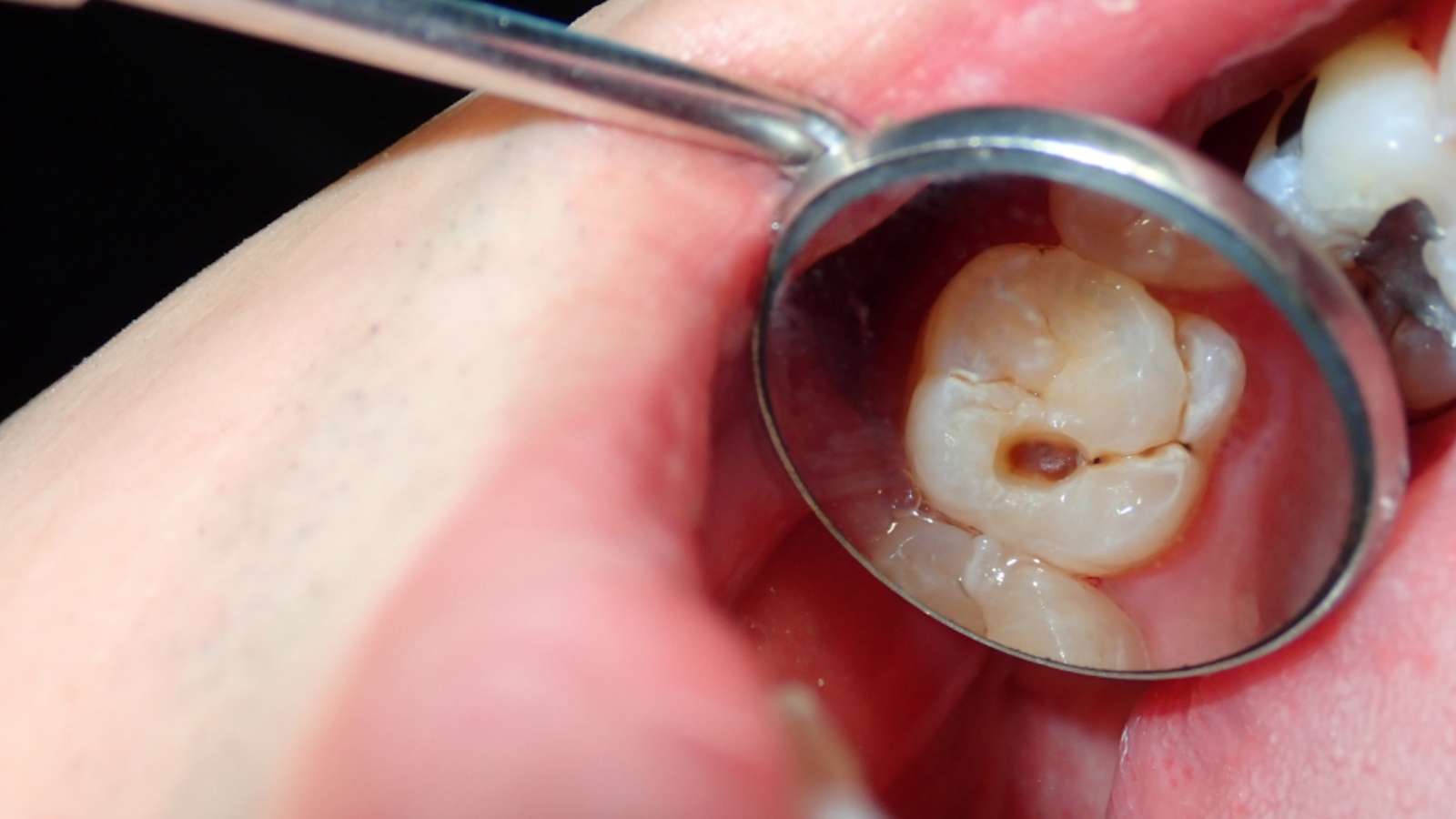
Involvement of cavities on the mesial and distal surfaces of back teeth.
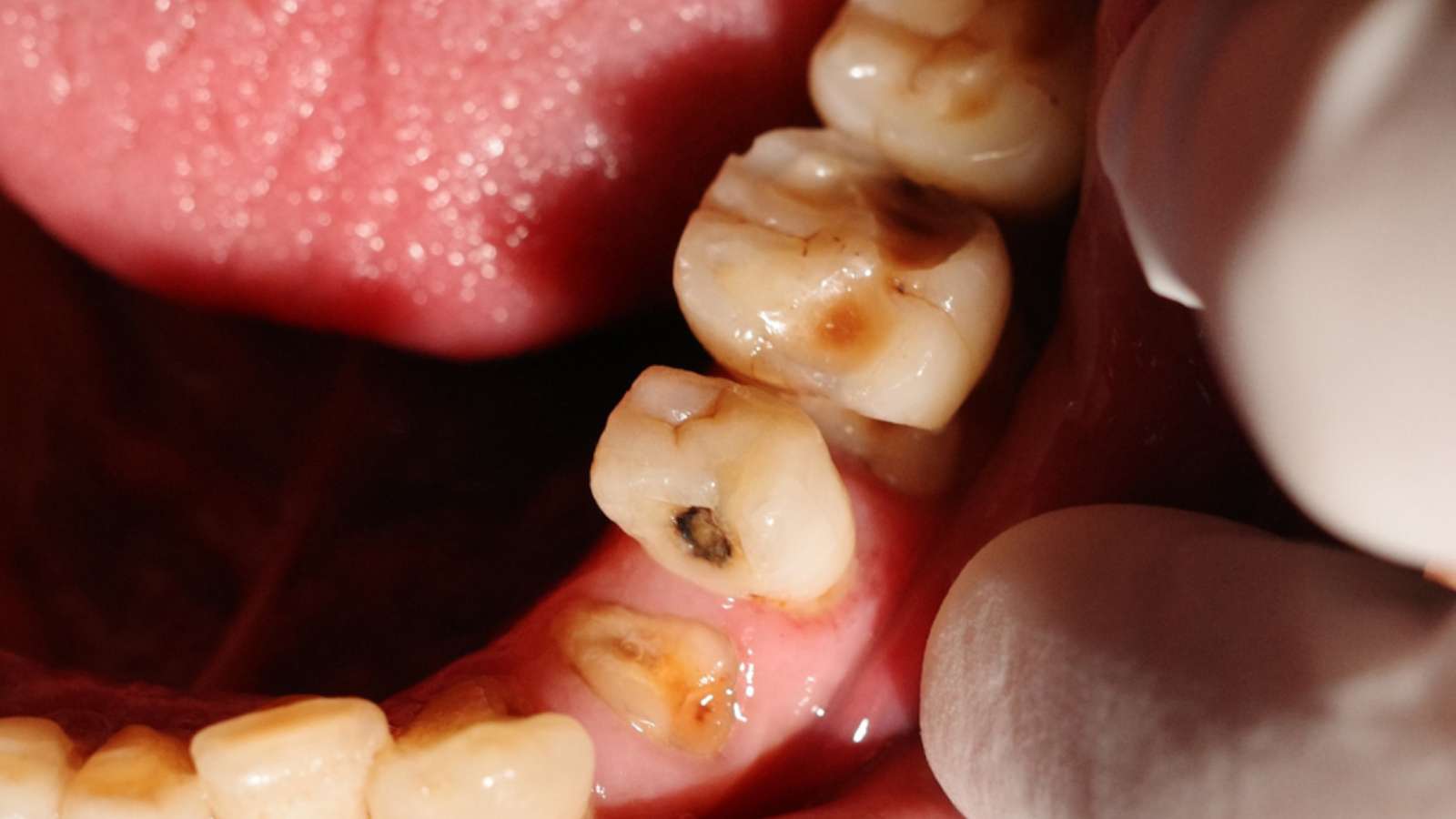
Involvement of cavities on the mesial and distal surfaces of front teeth.
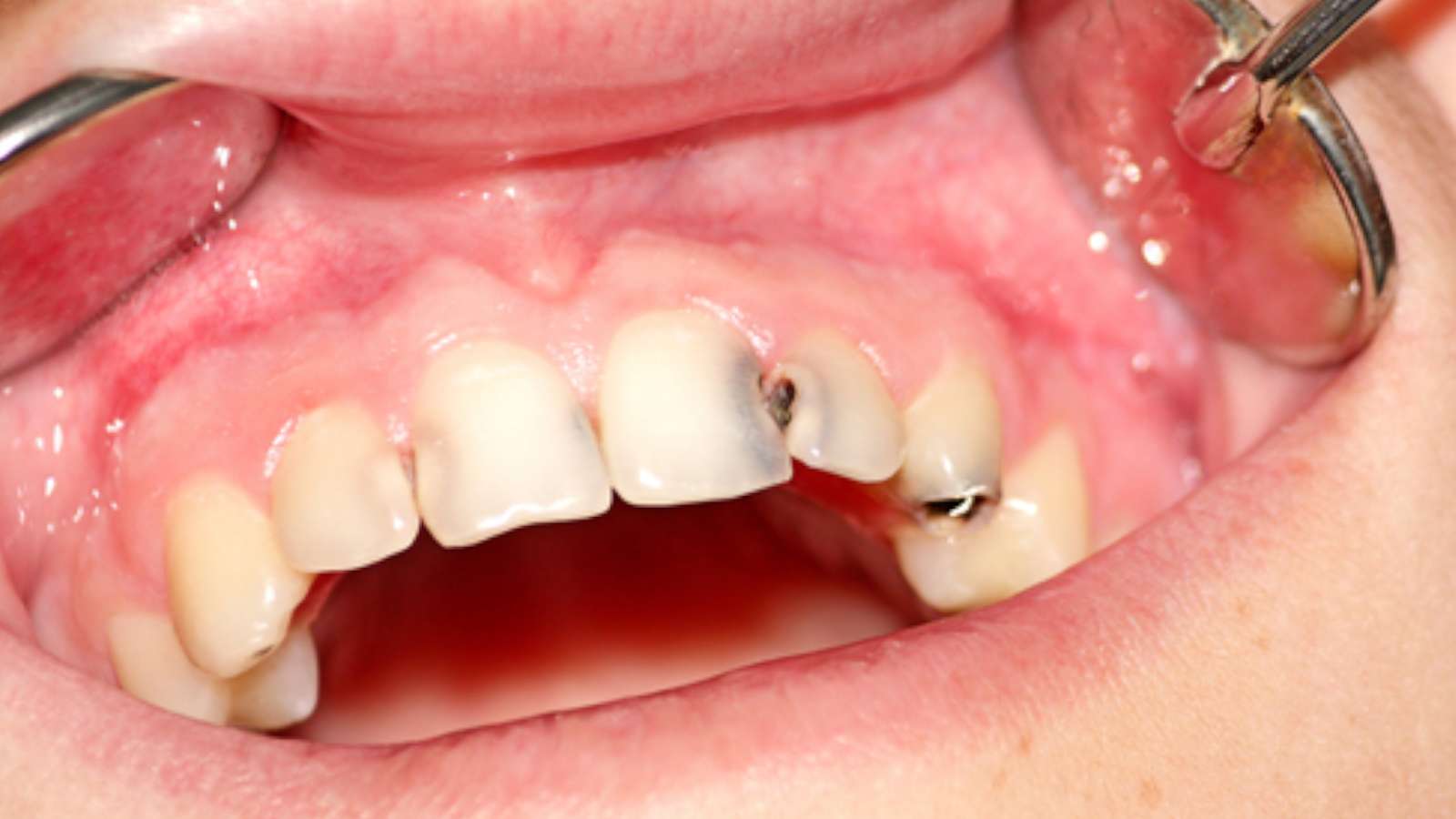
Involvement of cavities on the front teeth's mesial, distal surfaces and incisal edges.
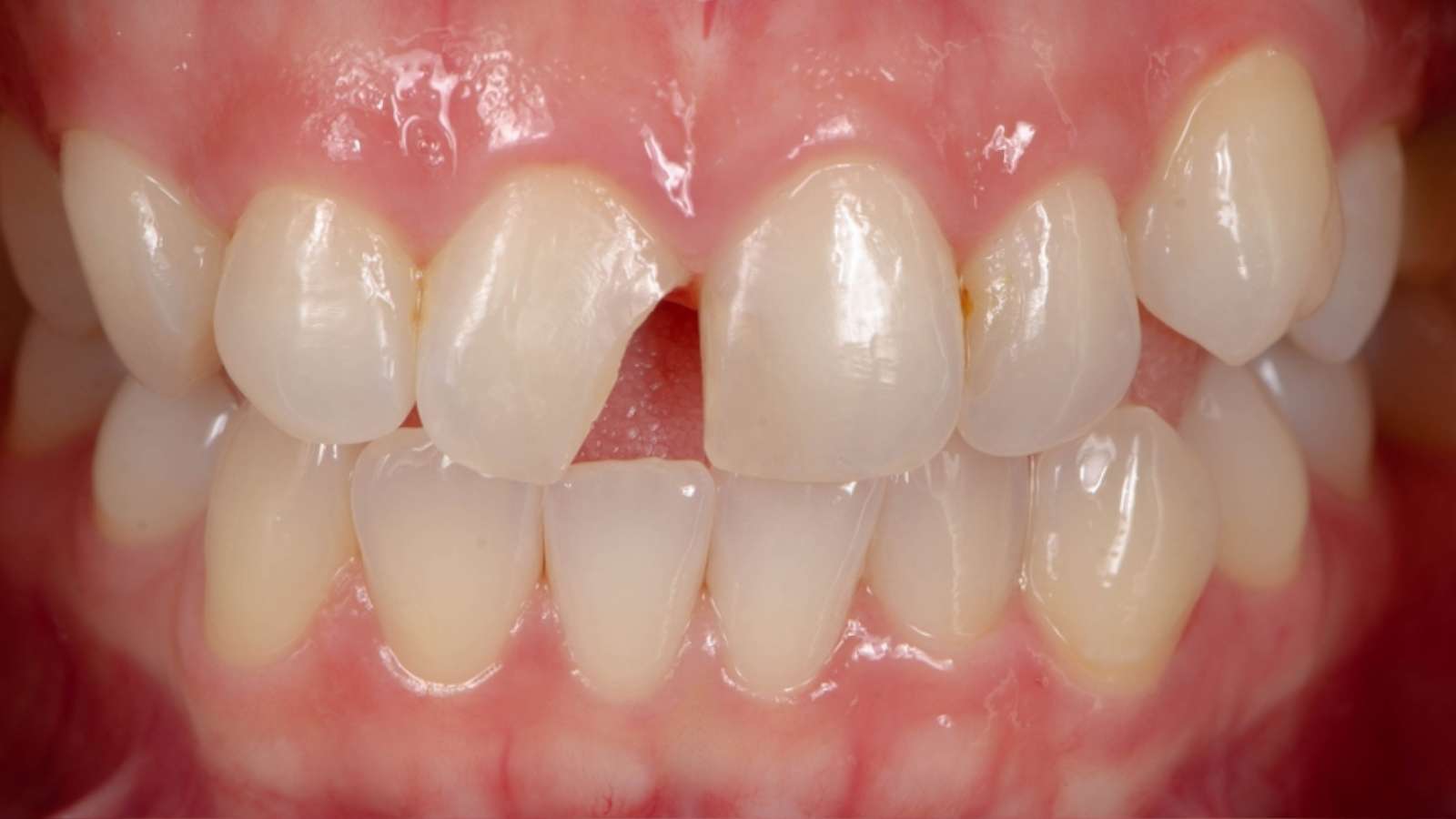
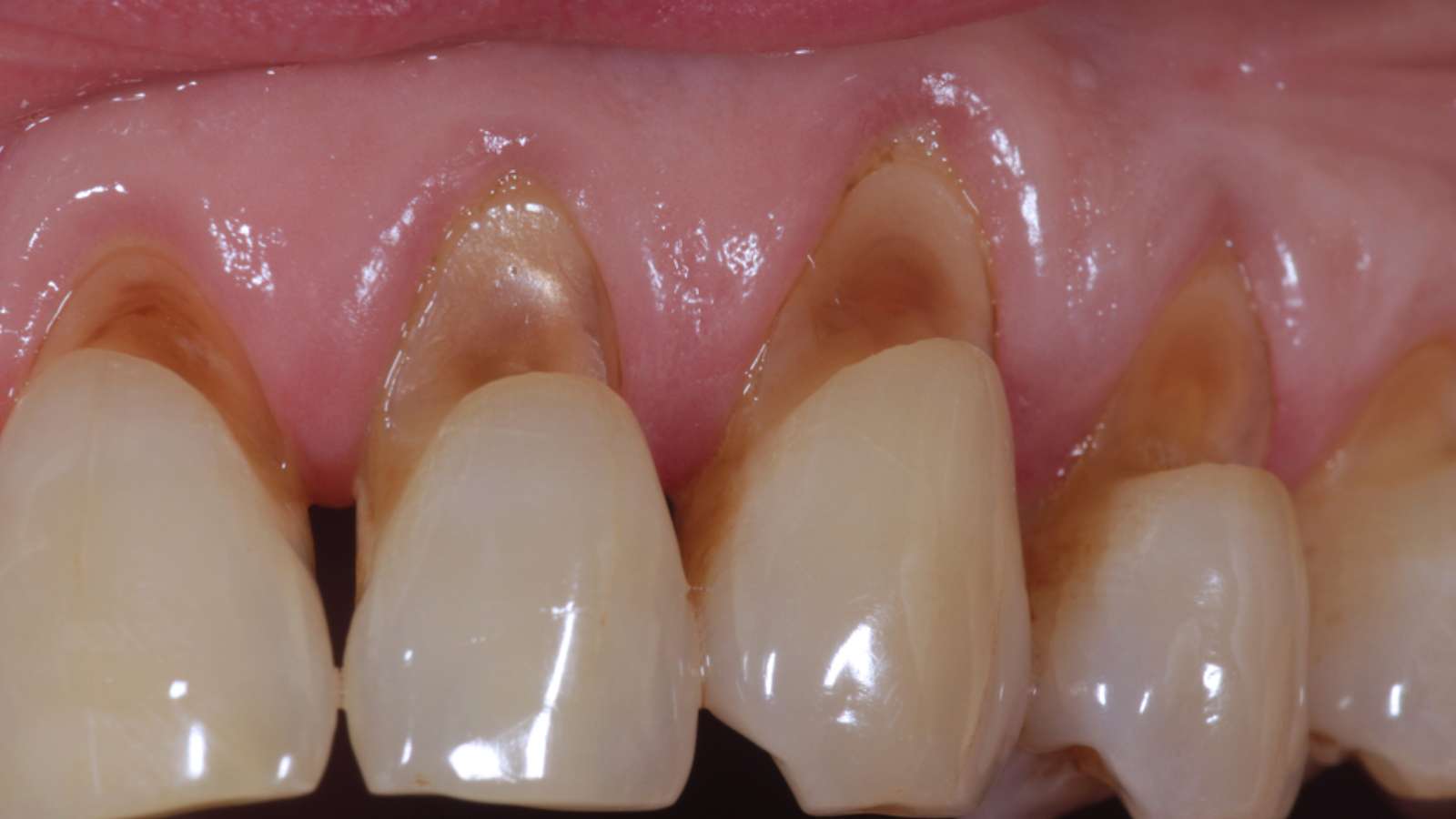
Involvement of cavities in the cervical areas of incisors, canines, premolars, and molars.